Wonders of Handloom
Fabrics is woven by loom.
Traditional loom is made from wooden planks with by a comb like device for holding the individual fibers (threads) apart.
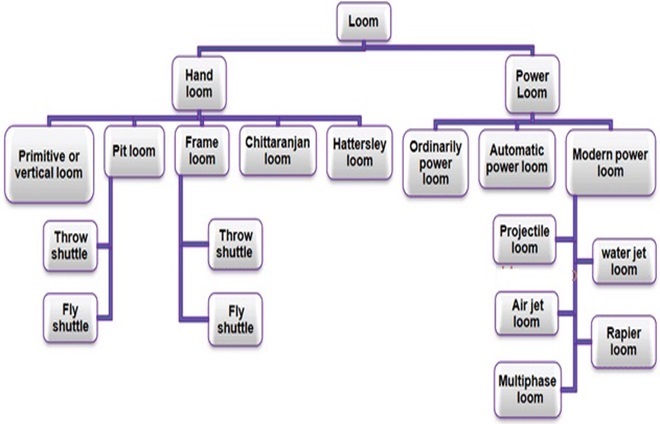
Broadly of two categories –
- Handloom- operated by hand.
- Power loom – operated by machine.
Handloom are of
- Primitive – loin loom
- Pit loom
- Frame Loom
“Loom” for weaving fabrics
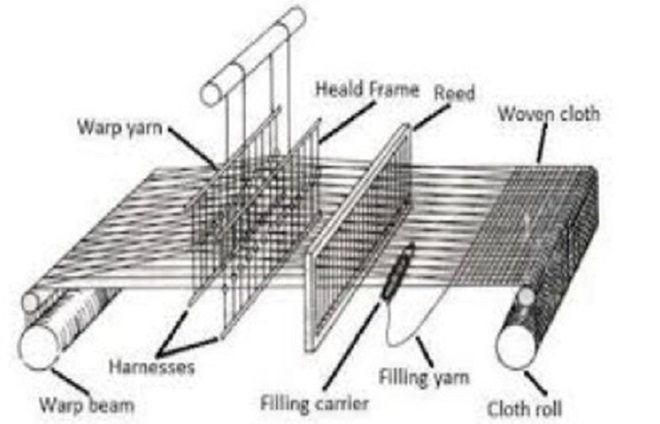
- A machine or device, which is used for weaving or interlacing two sets of yarn and thread into fabrics.
- The longitudinal (length wise) yarn is called warp (tana) which is interlaced with horizontal (breadth wise ) yarn called weft (Bana).
- The twisted warp threads are held in the loom under pressure to enable the progress of the interweaving of the weft strands.
- Each thread in the warp passes through a heddle, which is used to separate the warp threads for the passage of the weft.
- The heddle is made of cord or wire and is suspended on a shaft of a loom.
- Each heddle has an eye in the center. where the warp is threaded through.
- Each shaft or harness controls a set of threads.
- Raising or lowering several shafts at the same time gives a huge variety of possible gaps, through which the shuttle containing the weft thread can be thrown.
- Reed is a metallic comb, which is fixed to Sley with a Reed cap. The stick of Reed is called Split and the space between two-wire is known as Dent.
- Reed of two types (i) Bamboo Reed and (ii) Steel or Brass Reed.
Primitive Loom
Back strap / Loin / Kamar tanta
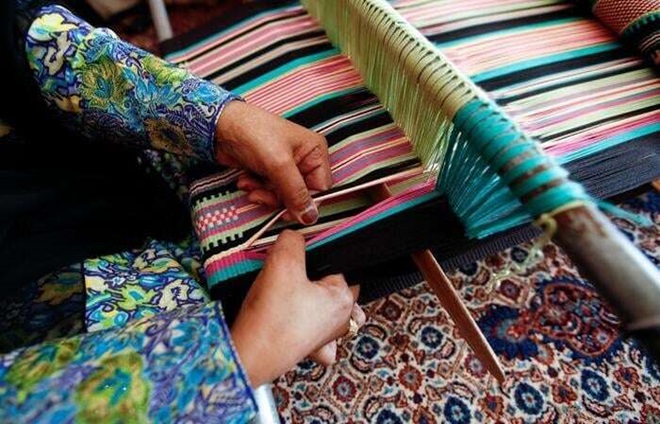

- Simplest type of loom
- Made from few pieces of bamboo or wood
- One end is tied to a tree or pillar
- Weight of the weaver is used to create tension and facilitate weaving
- Common to the tribal households of the Northeastern sates
- Each woman has her own loom and weave her own dress
- Usually of narrow width
- Non-commercial, domestic use
- Store house of design
- Efforts for diversifying use
Pit Loom
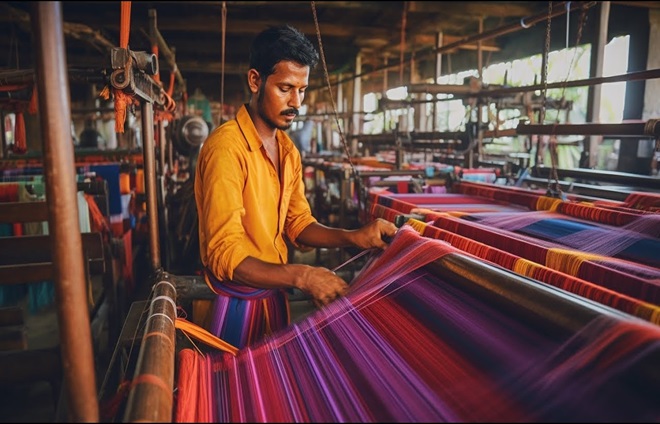

- Pit loom is mounted on a wooden frame, made of wooden planks. The weaver seats at the ground level, with his legs below in a pit .
- Costs relatively less and hence affordable.
- Low height of the house in the rural area enable the weavers to fix designing devices above it.
Frame Loom
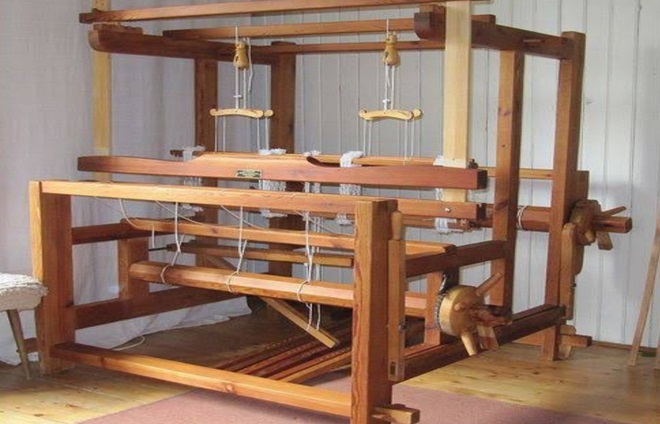

- Made of wooden planks
- Has proper arrangement fo lseating of the weaver at a raised level
- Keeping legs are at the ground level
- Sturdy, convenient, costs more
- Fixing of designing device lbecomes easy
Chittaranjan Handloom
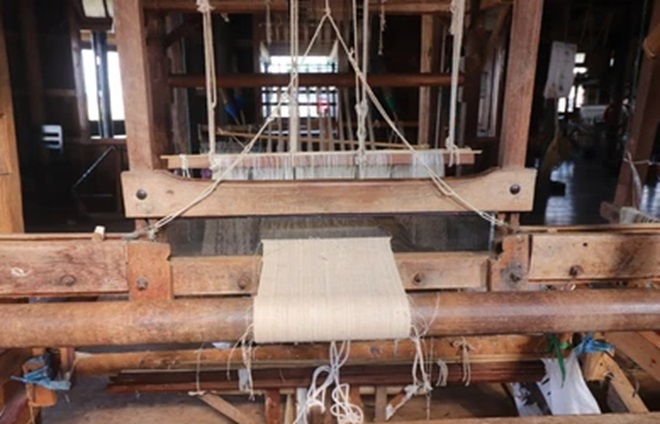

- Semiautomatic loom, sturdy construction, made of iron and wood, commonly used in Bengal
- Principal characteristic-in its beating up take up and let off motion
- For beat up, two wheels upon the top shaft connect the slay at two ends with two levers
- A five wheel positive take-up motion has been adopted to regulate pics per inch
- Shedding & picking motion in this loom work as fly shuttle loom.
- Production rate is high.
Handloom of India
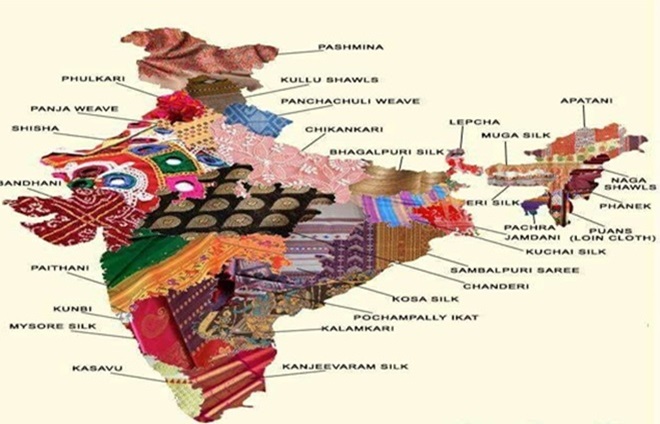
A part of the glorious tradition and culture.
Each region having handloom with its unique features represents “Unity in Diversity”
is of enormous socio-economic significance.
Looms – 23.77 lakh (2019)
- 87% in rural area
- 77%women
- mostly loin looms for personal use / domestic
- 95%of world’s handlooms are in India
- 15,000 cooperative societiesProduction 7,990 million sq. Meters (2018-19)
Handloom of Odisha
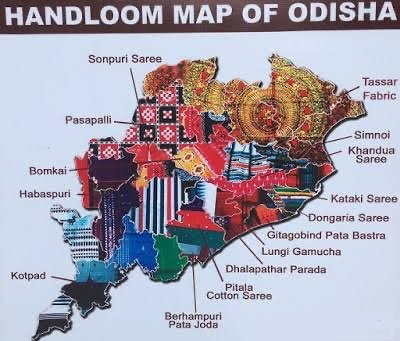
Geographical Regions –
Handloom is practices by weavers living in geographical clusters. Major centre of Handloom production in Odisha located on either sides of the River Mahanadi
- Sonepur,
- Baragarh,Sambalpur,
- Kalahandi
- Maniabandh,Nuapatna,
- Jagatsingpur
- SouthBerhampur- know as the Silk city
- Gopalpurof Cuttack tassar weaving
- Kotpadof Korpaut – tribal design with natural dyes
Handloom fabrics – types
- Resistdyed – Tie & dye (Bandha)
- Extrawarp and extra weft
- Painted
- Printed
Handloom of the Northeastern Region
Comprised of Seven states namely Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura and Mizoram
Commonly described as “Land of Seven Sisters “ because of
- their being a part of the contiguous geographic region and
- Interdependence on each other,
- similarities in the political, social and economic spheres notwithstanding ethnic and religious diversity
Formed under The North Eastern Areas (Reorganisation) Act, 1971 Sikkim was added to NER in 1987
- Making NER a group of eight states in the north eastern part of India
NER has its unique features –
- Not only for its location- geographically isolated ( separated from the mainland by erstwhile East Pakistan now Bangladesh)
- But also culture, tradition, music, dance, religion, festivals as well as
- Wide and diverse range of hand-women fabrics ( handloom) with color and designs specific to each region and tribes .
Typical features of Handloom of NER
Broadly of two categories
Domestic/personal use-
- Intricately woven loin loom weavers of the hill tribes and the different communities,
- which inhabit in Mizoram, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura and Arunachal
- Narrow width
Commercial scale production
- Sophisticatedand distinctive golden muga silk and mekhola chador of Assam
- introduced by the Bodo tribes ( who migrated from central Asia)
Handloom of the North Eastern states
Handlooms of the hill tribes Weave on back strap or loin looms fabrics for personal use

Handlooms of the hill tribes Weave on back strap or loin looms fabrics for personal use

